Income Tax Withholding Tracker February 27, 2026
Income tax withholding in February came in $179 million (2 percent) above budget projections and 4 percent higher than last year. The past few months have seen more modest withholding growth compared to last fall. Zooming out to cover December, January, and February, the 3-month withholding total was just 3 percent higher than during the same period one year ago.
Cannabis Tax Revenue Update (2025 Q4) February 26, 2026
The administration currently estimates that retail excise tax revenue was $145 million in the fourth quarter of calendar year 2025 (October through December). With this latest data, we currently project cannabis tax revenues of $648 million in 2025-26. This is $36 million above the January Governor’s Budget forecast for 2025-26.
Updated "Big Three" Revenue Outlook February 20, 2026
Near-Term Revenue Outlook Improved but Future Challenges Remain. Our updated forecast anticipates revenues from the state’s three largest taxes (income, corporation, and sales) are likely to come in ahead of Governor’s Budget assumptions in the current year and about in line with assumptions in the budget year. This upgraded outlook is entirely attributable to higher expectations for income tax collections, which are being driven by enthusiasm around AI and the related stock market boom. As such, we continue to caution that these surging revenues likely are not sustainable. Our revenue outlook for 2027-28 and beyond remains similar to our November Fiscal Outlook, continuing to reflect the high risk of a revenue reversal. Under these revenues, our Fiscal Outlook estimated that the state would face structural deficits of around $35 billion annually starting in 2027-28.
The 2026-27 Budget: How to Use One-Time Revenue Improvements February 20, 2026
Recent stock market performance continues to boost income tax collections. In our Fiscal Outlook, we strongly advised the Legislature to treat near-term strength in tax collections as temporary because we expect these gains to reverse. Further, the state faces significant structural deficits in the future. Accordingly, any windfall received from this revenue uptick represents an opportunity for the Legislature to prepare for future fiscal challenges.
Inflation Tracker February 20, 2026
December data for the US show annual inflation remained above pre-pandemic averages with the downward trend seen since mid-2022 stalling. While a lapse in appropriations for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) during October and November 2025 led to concerns about the accuracy of November and December inflation statistics, estimates suggest similar inflation levels to previous months. Between December 2024 and December 2025, prices for US consumers grew by 2.7% and prices for CA consumers grew by 3.2%. However, it is likely that wage growth exceeded inflation in 2025. Growth in the price of consumer goods seen in early and mid-2025 has largely reversed, with goods prices falling slightly between January 2025 and January 2026. Consumer expectations about inflation in the next one to five years spiked in early 2025 but have since declined, nearly to pre-2025 levels.
Firearms and Ammunition Revenue Update (2025 Q4) February 18, 2026
For firearm and ammunition excise tax returns filed for the fourth quarter of 2025, the total amount of tax due is $16 million.
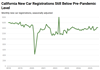
California New Car Registrations: December 2025 February 9, 2026
Registrations Fell Slightly in December. Seasonally adjusted new car registrations declined by 1 percent in December. After three weak months, registrations are now 5 percent below the average level over the last couple of years.
Monthly Jobs Report (December) January 30, 2026
Payroll Employment Now Lower Than it Was a Year Ago. California's traditional jobs report shows the state lost 2k jobs in December after gaining 31k jobs in November. The November figures were the first meaningful statewide job gains since May. With this month's figures, the state has technically lost employment overall since a year ago, a first since the pandemic began. Employment numbers from a secondary source, a household survey of workers, have trended more positive since September but are set to be revised substantially with next month's data release.
California Housing Affordability Tracker (4th Quarter 2025) January 22, 2026
Our post provides an updated snapshot of housing affordability in California. Over the last few years, we have seen a rapid increase in California housing costs, led by the dramatic increase in the costs of purchasing a home. Despite no significant growth in housing prices since 2024, monthly costs for a newly purchased home are about $2,400 higher than they were just a few years ago. This increase is driven both by increases in home prices between 2020 and 2022 and an increase in mortgage rates since 2022.
The rapid increase in mortgage rates in 2022 has also left most existing homeowners "locked-in" to mortgages with rates significantly lower than currently available. Almost 80 percent of California homeowners have mortgage rates under 5 percent, compared to current rates of about 6.25 percent. These homeowners face a significant additional financial cost to moving, further limiting the number of homes available for sale.
California New Car Registrations: November 2025 January 6, 2026
Registrations Dropped in November. Seasonally adjusted new car registrations declined by 4 percent in November. After two weak months, registrations are now 4 percent below the average level over the last couple of years.
2025 Update: Tech Company Stock Pay Accounts for One-Quarter of Withholding Growth So Far in 2025-26 December 3, 2025
California's technology companies, including Apple, Google, Nvidia, Meta, and Broadcom are the most valuable companies in the world and employ thousands of highly-paid workers in the state. Many employees at these companies receive equity pay, such as stock options and restricted stock units, in addition to their base salary. As we first pointed out two years ago, state income tax withholding on stock pay has grown to more than $10 billion annually due to the AI boom in asset prices for these companies. With updated data through 2025Q3, we now believe growing withholding from these sources accounted for a quarter of the strong income tax withholding growth seen in the first three months of 2025-26.
California New Car Registrations: October 2025 December 3, 2025
Registrations Dropped in October. Seasonally adjusted new car registrations declined by 2.4 percent in October. October registrations were 5 percent lower than recent peaks in December and April but slightly higher than the average level over the last couple of years.
Cannabis Tax Revenue Update (2025 Q3) December 2, 2025
The administration currently estimates that retail excise tax revenue was $177 million in the third quarter of calendar year 2025 (July through September). This is the highest quarterly total since the state eliminated the cultivation tax. With this latest data, we currently project cannabis tax revenues of $631 million in 2025-26, nearly $100 million below the budget assumption for 2025-26.
Firearms and Ammunition Revenue Update (2025 Q3) November 18, 2025
Beginning July 2024, Chapter 231 of 2023 (AB 28, Gabriel) imposed an 11 percent excise tax on retail sales of firearms, firearm precursor parts, and ammunition, with some exemptions. Current tax return data suggest that the revenues from this tax will total around $58 million for 2024-25. Further, tax returns filed for the third quarter of 2025 show total tax due of $13 million—slightly below the quarterly average in the first year of the program.
California New Car Registrations: September 2025 November 14, 2025
Registrations Flat in September. Following three straight months of substantial growth, seasonally adjusted new car registrations grew just 0.1 percent in September. This is 3 percent lower than recent peaks in December and April but somewhat higher than the average level over the last couple of years.